
About Us
What is FallScreen©?
FallScreen© is a falls risk calculator and has two forms: a short form and a long form. The short form is designed as a screening instrument suitable for General Practice surgeries, acute hospitals, and long-term care institutions. It takes only 15 minutes to administer and contains five items: a single assessment of vision, peripheral sensation, lower limb strength, reaction time and body sway.
The long form is designed as a comprehensive instrument suitable for Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy settings and for dedicated Falls Clinics. It takes 45 minutes to administer and contains 15 items: three assessments of vision (high and low contrast visual acuity and edge contrast sensitivity), three assessments of peripheral sensation (tactile sensitivity, vibration sense and proprioception), assessments of three lower limb muscle groups (knee extensors, knee flexors and ankle dorsiflexors), assessments of both hand and foot reaction time and four assessments of body sway (sway on floor and foam with eyes open and closed).
Prof Stephen Lord's Physiological Profile Assessment (PPA) has been marketed through Neuroscience Research Australia (formerly the Prince of Wales Medical Research Institute) as POWMRI FallScreen®. These tools are now used in over 150 research and clinical settings within Australia and across the world, Belgium, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, Korea, Malta, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Singapore, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, USA and UK.
Click here to download an article on the Physiological Profile Assessment
The physiological assessments
Visual function is measured using a dual contrast visual acuity chart, the "Melbourne Edge Test" and a device for measuring depth perception. Lower limb sensation is assessed with tests of proprioception, touch sensitivity and vibration sense. The strength of three muscle groups in both legs is measured: the knee flexors and extensors and ankle dorsiflexors. Simple reaction time is assessed using movement of the finger as the response, and choice reaction time is assessed using a step as the response. Body sway on a firm and compliant (foam rubber) surface with eyes open is assessed using a swaymeter that measures displacements of the body at the level of the waist.
These assessments are simple, 'low-tech' and readily accepted by older subjects. All have high external validity and test-retest reliability and are described in detail in our published papers (1-7). When combined in multivariate discriminant analyses, we have found that these tests can predict those at risk of falling with 75% accuracy in both community and institutional settings.
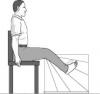
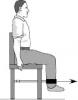
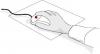
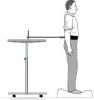
Short form tests
| Contrast sensitivity | Proprioception | Lower limb strength | Reaction time | Postural sway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The FallScreen© internet program
For both the short and long forms, a computer software program assess each person's performance in relation to the normative database complied from large population studies (6,7). The program produces a falls risk assessment report for each subject which includes the following four components:
- a graph indicating the person's overall falls risk score,
- a profile of individual test performance results,
- a table indicting individual test performances in relation to age-matched norms,
- a written report which explains the results and makes recommendations for improving performances and compensating for any deficit areas identified.
The graph indicating the person's overall falls risk score is a single index score based on a discriminant function analysis developed for our research studies which accurately discriminates between elderly fallers and non-fallers. This graph presented the person's falls risk score in relation to persons of the same age and in relation to falls risk criteria ranging from low to extreme.
The profile of test performance results presents the subject's scores in each of the tests in standard (z score) format. As the scores have been standardised the test results can be compared with each other. The table indicting individual test performances in relation to age-matched norms also identifies deficit areas.
Finally, the written report summarises the findings and makes individual recommendations for reducing falls risk. It provides an excellent basis for targeting interventions to improve or compensate for impairments in the following physiological domains: strength, balance, speed and co-ordination, vision, peripheral sensation and therefore reduce the risk of falling in older people.
How to obtain a license to use FallScreen©
For information about obtaining the test devices, instructor training and internet access to FallScreen©, email: fallscreen@neura.edu.au. Click here for more details about falls assessment kits.
References
- Lord SR, Clark RD, Webster IW. Postural stability and associated physiological factors in a population of aged persons. J Gerontol 1991;46:M69-76.
- Lord SR, Castell S. The effect of a physical activity program on balance, strength, neuromuscular control and reaction time in older persons. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1994;75:648-652.
- Lord SR, Clark RD, Webster IW. Physiological factors associated with falls in an elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc 1991;39:1194-1200.
- Lord SR, McLean D, Stathers G. Physiological factors associated with injurious falls in older people living in the community. Gerontology 1992;38:338-346.
- Lord SR, Clark RD. Simple physiological and clinical tests for the accurate prediction of falling in older people. Gerontology 1996;42:199-203.
- Lord SR, Ward JA, Williams P, Anstey K. Physiological factors associated with falls in older community-dwelling women. J Am Geriatr Soc 1994;42:1110-1117.
- Lord SR, Sambrook PN, Gilbert C, Kelly PJ, Nguyen T, Webster IW, Eisman JA. Postural stability, falls and fractures. Results from the Dubbo Osteoporosis Epidemiology Study. Med J Aust 1994;160:684-691.
A summary of this research and a demonstration of FallsScreen can be found in the following paper: Lord SR, Menz HB, Tiedemann A. A physiological profile approach to falls risk assessment and prevention. Physical Therapy 2003;83:237-252. PDF
Related Downloads
NB: By accessing this software, you acknowledge that you have read, understood and agree to the Terms of Sale and Licence Agreement accompanying this software.